Sailing, a timeless art and sport, has seen numerous technological advancements and design innovations over the years. Among the most critical components of a sailboat are the sails themselves, specifically the Genoa and Jib sails. These two types of headsails play a vital role in maneuvering and performance, each with unique characteristics and applications.
A Genoa sail, often referred to as an overlapping sail, is a large foresail that extends past the mast, providing increased sail area. It’s particularly effective in light wind conditions, where maximizing the surface area exposed to the wind is crucial. The Genoa’s design, size, and trimming are essential factors in harnessing wind power efficiently.
On the other hand, a Jib sail, known as a non-overlapping sail, is typically smaller and easier to handle, especially in strong wind conditions. The jib’s size, shape, and material contribute to its functionality, making it an essential part of the sailboat’s rigging.
Historical Context
The evolution of these sails can be traced back to the early days of yachting. The Genoa sail, named after the Italian city of Genoa, revolutionized sailing performance with its overlapping design. The jib, with its various sizes and cuts, has been a staple in sailing, offering versatility and ease of handling.
Importance in Modern Sailing
In modern sailing, the choice between a Genoa and a jib is not merely a matter of preference but a strategic decision based on factors such as wind conditions, sailing techniques, and the sailor’s experience level. Whether it’s a leisurely sail on a calm lake or a competitive yacht race in challenging marine weather, understanding the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of these sails is paramount.
From sail shape to sail maintenance, from tacking to gybing, the Genoa and jib are integral to sailing performance. They represent not only the heritage of sailing but also the ongoing innovation and technological advancements in yacht design and sailing equipment.
This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of Genoa vs. Jib, delving into their characteristics, differences, and practical considerations for sailors. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice eager to learn, the following sections will provide valuable insights into these essential components of sailing.
Description and Characteristics of Genoa and Jib sails
Genoa Description
Shape and Size
The Genoa sail is known for its large size and unique shape, often overlapping the mainsail. This overlapping design allows for a greater sail area, enhancing the sailboat’s performance in light wind conditions. The Genoa’s size is measured as a percentage of the foretriangle, with larger Genoas providing more power but requiring careful handling.
Overlapping the Mainsail
The overlapping characteristic of the Genoa sail is what sets it apart from other headsails. By extending past the mast, it captures more wind, translating into increased speed and maneuverability. This design requires precise trimming and rigging to optimize performance.
Measuring Genoas
Genoas are categorized by their size relative to the foretriangle of the sailboat. A 150% Genoa, for example, means that the sail’s area is 150% of the foretriangle. Understanding the measurements and choosing the right Genoa for specific wind conditions is essential for optimal sailing performance.
Jib Description
Shape and Function
The Jib sail, unlike the Genoa, does not overlap the mainsail. Its smaller size and non-overlapping design make it easier to handle, especially in strong wind conditions. The jib’s shape and function are integral to the sailboat’s tacking and gybing, providing control and stability.
Sizes and Types
Jibs come in various sizes and types, each suited for different sailing conditions. From storm jibs, designed for heavy weather, to working jibs used for everyday sailing, understanding the different types of jibs and their applications is crucial for sailors.
Role in Maneuvering the Boat
The jib plays a vital role in maneuvering the sailboat, especially during tacking and gybing. Its size, cut, and material contribute to the boat’s responsiveness and control, making it an indispensable part of modern sailing.
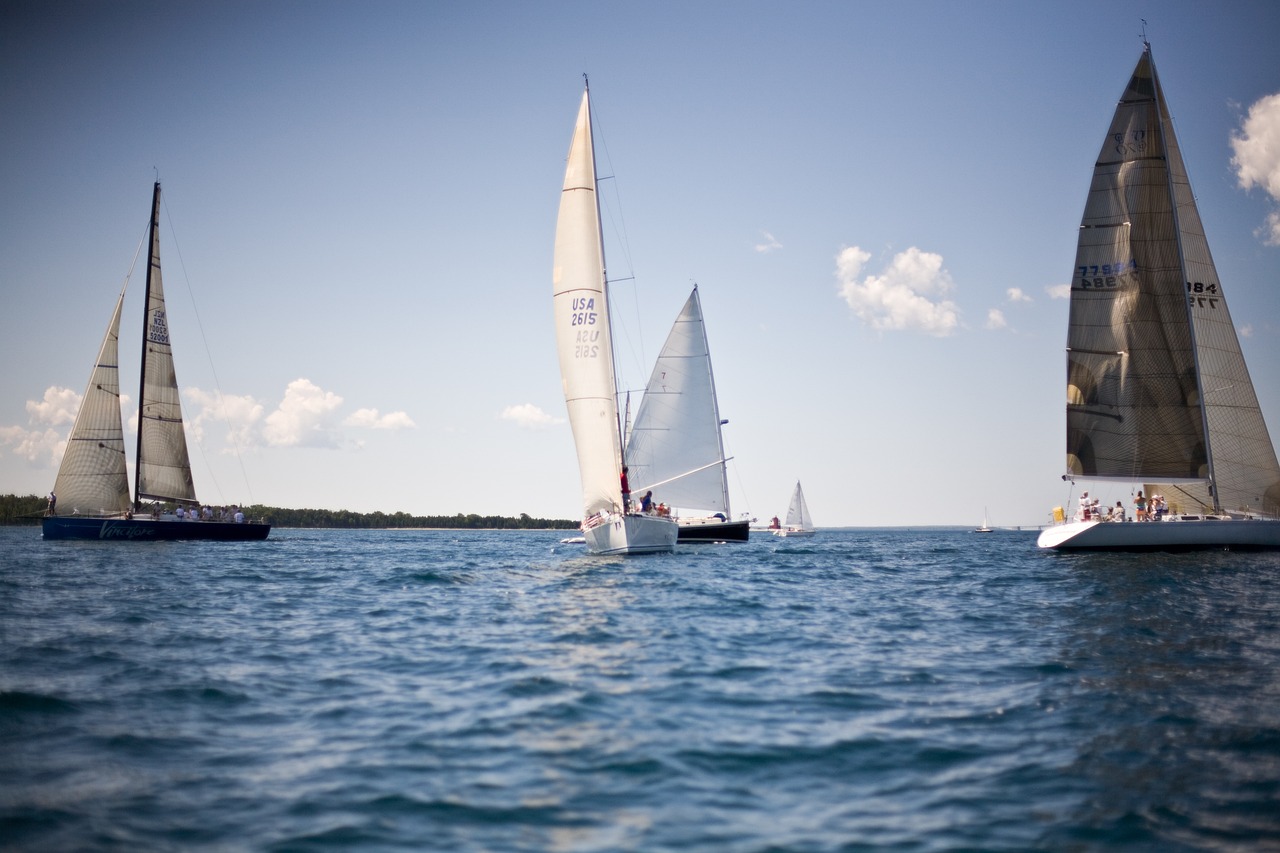

Differences Between Genoa and Jib
Size and Overlap
The most apparent difference between Genoa and Jib sails lies in their size and overlap. A Genoa sail is larger and overlaps the mainsail, extending beyond the mast. This design allows for more sail area, capturing more wind, and enhancing performance in light wind conditions. In contrast, a Jib sail is smaller and does not overlap the mainsail, making it more manageable, especially in strong winds.
Weight and Handling
The weight and handling of these sails also differ significantly. A Genoa’s larger size means it’s generally heavier and requires more effort to handle, especially during tacking and gybing. It may necessitate additional crew members or specialized equipment like roller furling systems. On the other hand, the jib’s smaller size and non-overlapping design make it lighter and easier to manage, even for single-handed sailors.
Usage in Different Wind Conditions
Genoa and Jib sails are suited for different wind conditions. A Genoa’s larger sail area makes it ideal for light to moderate winds, where it can harness more wind power to propel the boat. In contrast, a jib’s smaller size and ease of handling make it suitable for strong winds, where control and stability are paramount. Sailors must consider these differences when selecting the appropriate sail for their journey, taking into account factors like wind direction, sailing techniques, and the sailboat’s rigging.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Genoa and Jib sails
Advantages of Genoa
Light Wind Performance
The Genoa’s large size and overlapping design make it an excellent choice for light wind conditions. By capturing more wind, it can propel the sailboat even when the breeze is minimal, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable sailing experience.
Increased Sail Area
The increased sail area of the Genoa provides more power, allowing for faster speeds and better upwind performance. This advantage makes the Genoa a popular choice among racers and cruisers alike, seeking to maximize their sailing efficiency.
Advantages of Jib
Strong Wind Performance
The jib’s smaller size and non-overlapping design make it ideal for strong wind conditions. It offers better control and stability, reducing the risk of overpowering and ensuring a safer sailing experience.
Ease of Handling
The jib is generally easier to handle, especially during tacking and gybing. Its design allows for quicker adjustments and requires less physical effort, making it suitable for single-handed sailors or smaller crews.
Disadvantages and Challenges
Handling Difficulties
While the Genoa offers many advantages, its large size can also present handling difficulties, especially in unexpected wind shifts or for inexperienced sailors. It may require specialized equipment or additional crew members to manage effectively.
Maintenance and Cost
Both Genoa and jib sails require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The Genoa’s larger size may lead to higher maintenance costs and potential wear and tear. Additionally, having both sails in the sail inventory can increase overall expenses for sailors.
Practical Considerations when Buying New Sails
Selecting the Right Sail
Factors to Consider
Choosing between a Genoa and a jib requires careful consideration of various factors, including wind conditions, sailing techniques, geographic location, and the sailor’s experience level. The right sail can enhance performance, safety, and enjoyment on the water.
Geographic Location and Experience Level
The choice may also depend on the specific sailing location and the sailor’s skill level. For example, a Genoa might be preferred in areas known for light winds, while a jib might be more suitable for strong wind regions or for less experienced sailors.
Sail Inventory and Multiple Sails
Benefits of Having Different Sails
Having both Genoa and jib sails in the sail inventory offers flexibility and adaptability to various sailing conditions. It allows sailors to switch between sails as needed, optimizing performance and control.
Changing Sails According to Conditions
Understanding when to use a Genoa vs. a jib and how to change sails according to wind conditions is a valuable skill. It requires knowledge of sail shape, rigging, and sailing equipment, ensuring a seamless transition between sails.
Technological Advancements
Roller Furling Headsails
Modern sailing has seen technological advancements like roller furling headsails, which allow for easier handling of both Genoa and jib sails. This technology simplifies the process of furling and unfurling the sails, making it accessible to sailors of all experience levels.
New Design Considerations
Innovations in sail design, material, and construction have also contributed to the versatility and efficiency of Genoa and jib sails. These advancements provide more options for sailors, enhancing the sailing experience and reflecting the ongoing evolution of the sport.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Summary of Key Differences
The comparison between Genoa and Jib sails reveals distinct differences in size, overlap, weight, handling, and usage in various wind conditions. While the Genoa’s larger size offers advantages in light winds, the jib’s smaller, non-overlapping design provides control in strong winds. These differences influence the choice of sail, sailing performance, and the overall sailing experience.
Practical Recommendations for Sailors
Understanding the differences between Genoa and jib sails empowers sailors to make informed decisions. Here are some practical recommendations:
- When to Use Genoa vs. Jib: Consider wind conditions, sailing techniques, and experience level when selecting the appropriate sail.
- Maintenance Tips: Regular maintenance, including inspection for wear and tear, ensures optimal performance and longevity of both sails.
- Invest in Technology: Consider investing in technologies like roller furling headsails to enhance ease of handling.
Future Trends and Innovations
The world of sailing continues to evolve, with innovations in sail design, material, and technology. Future trends may include:
- Sustainable Materials: Eco-friendly materials for sails that reduce environmental impact.
- Smart Sailing Technology: Integration of sensors and automation to optimize sail performance.
- Customized Sail Design: Personalized sails tailored to individual sailing styles and conditions.
These trends reflect the ongoing innovation in sailing, connecting tradition with modernity, and offering new horizons for sailors.
Final Thoughts
The exploration of Genoa vs. Jib sails delves into the heart of sailing, uncovering the nuances, complexities, and joys of this timeless art. Whether a seasoned sailor or a novice eager to learn, understanding these sails’ characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and practical considerations enriches the sailing journey. It’s a journey that transcends mere sport, connecting us with nature, history, and ourselves. The sails may change, but the essence of sailing remains, an endless adventure guided by the wind, the waves, and the human spirit.
With this conclusion, the article offers a comprehensive understanding of Genoa and Jib sails, providing valuable insights and inspiration for sailors of all levels. It’s a tribute to the enduring legacy and vibrant future of sailing.